Grass Turning White: Causes + How to Fix the White Spots
White tips, spots, stripes, or patches on grass are usually signs of disease stress on your lawn. Taking control measures to fix the grass that’s turning white as soon as possible is key to recovering the lawn into a healthy state. Most of the fixes that work will depend on the cause and may include disease management, drought control, and correct application of fertilizer application. But why is your grass turning white and how do you fix it?
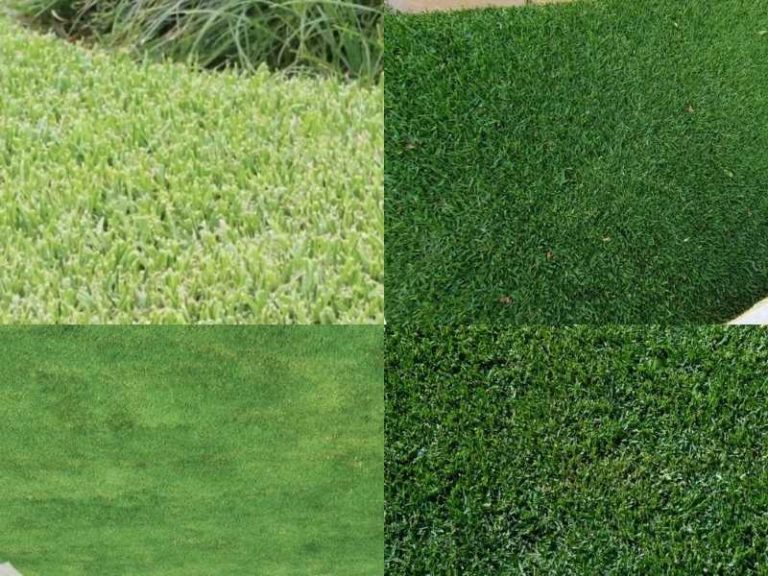
The most common reason for grass turning white is a fungal infestation called powdery mildew. Gray leaf spot and blight can also lead to white patches on the lawn. Apply a fungicide on the lawn to kill the fungus then increase sunlight exposure in shaded areas to prevent discoloration.
Why is my grass turning white?
Loss of color and whitening of grass blades is commonly caused by a variety of plant diseases such as powdery mildew, gray leaf spot disease, Fusarium patch, and Fusarium blight. Other factors that may also cause the grass to turn white include lawn mower damage, drought, fertilizer burn, and soil deficiencies.
Here are the possible reasons why your grass is turning white:
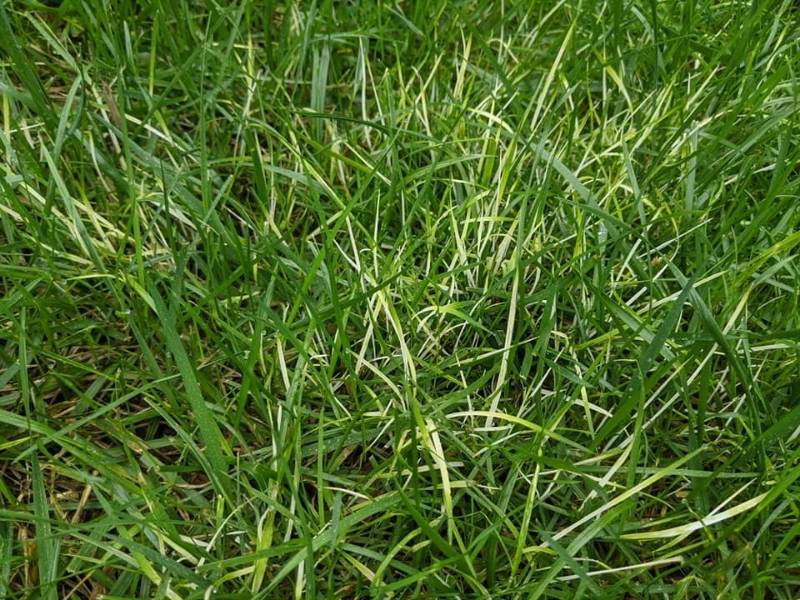

Powdery mildew
The most common reason grass turfs turn white is a lawn fungal disease called powdery mildew. This plant disease appears as white patches on grass blades, significantly diminishing the lawn’s visual appeal. The dust-like, white coverings (powdery mildew) are caused by a fungal organism known as Erysiphe graminis.
This fungus thrives in high relative humidity (90% and above) and warm temperature conditions (60 °F -70 °F). Low light intensity also favors the survival of Erysiphe graminis, thus your grass is more likely to develop powdery mildew if it’s growing under a shade. Also, powdery mildew infection only occurs when the weather is warm and dry.
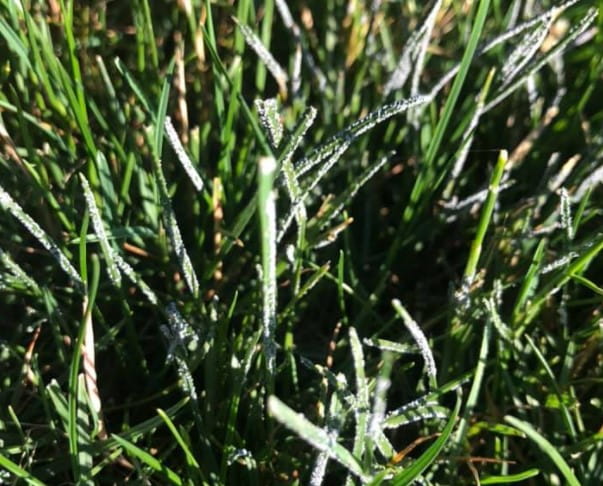

When conditions are most favorable, the fungus produces powdery spores on the grass blades, hence the name ‘powdery mildew’. Take note that young, developing grass (new sod) is more vulnerable to powdery mildew.
Note: Some turfgrass varieties such as Kentucky bluegrass are more susceptible to powdery mildew compared to others.
Gray leaf spot
Gray leaf spot disease also causes white or bleached spots on grass blades. This disease is caused by a fungus known as Pyricularia grisea. This fungus thrives in warm and high humidity conditions, as well as overwatered and overfertilized lawns. The whitish spots are usually accompanied by dark grass blade edges.
Gray leaf spot is common in warm-season turfgrass varieties like St. Augustine grass.
Fusarium patch and fusarium blight
Fusarium patch and Fusarium blight are two diseases caused by fungal organisms and cause a whitish/bleached appearance on certain types of grass at certain stages of infection. The latter is known to affect Kentucky bluegrass and starts off as gray-green circles before evolving into bleached patches of grass.
Fusarium patch, on the other hand, affects annual bluegrass, Kentucky bluegrass, and creeping bentgrass. It causes grass blades to appear soggy at the onset of infection before causing them to spot a bleached appearance later on.
While both fungal diseases thrive in heavily thatched lawns, Fusarium patch prefers cool conditions while Fusarium blight prefers warm weather conditions.
Herbicide side effect
In some cases, your grass may turn white after the application of selective herbicides to target specific grassy weeds in the lawn. For example, Tenacity Turf Herbicide is known to be a good crabgrass killer that’s safe for lawns but can bleach your turfgrass if not applied according to the instructions on the label.
I’d advise that you ALWAYS check the label for guidance on what turfgrasses the herbicide will be safe for. Also, adhere to the mixing and application instructions of herbicides such as 2,4-D to prevent bleaching your grass.
Lawn mower damage
Another common cause for grass discoloring and turning white is damage from a lawnmower. This happens when you cut your grass too short and remove too much of the grass blades resulting in a turf that can’t effectively photosynthesize to make its own energy. As the grass weakens, the blades fade in color, appearing whitish-grey.
Additionally, grass blade whitening may occur if you mow your grass with a lawnmower that has a blunt blade. The dull blade causes a frayed, pale white appearance at the top of the cut grass blades.
I would recommend a lawnmower that produces a clean cut if this is a problem you’re facing, such as the Fiskars Stay Sharp Max Reel Mower.
Pro tip: The whitening of grass caused by lawnmower damage is usually more prominent across the entire turf as opposed to powdery mildew that appears as sporadic white patches.
Drought
Though not a common cause, prolonged drought may also cause the tips of grass blades to appear frayed and turn white. This usually occurs during seasonal droughts when there’s no rainfall and the soil becomes too dry.
If you live in an arid or semi-arid region and don’t adequately irrigate your turf, the grass is at risk of developing white tips.
Mineral deficiencies and fertilizer burn
White marks on grass can also be caused by abiotic disorders such as fertilizer burns and mineral deficiencies in the soil. Fertilizer can burn your grass, resulting in white stripes on the grass blades a short while post-application.
Meanwhile, a lack of trace mineral iron in the lawn soil may also result in whitish/bleached spots on your grass blades, more so if your lawn soil is alkaline.
How to Fix White Grass in Your Lawn
To effectively fix white grass in your lawn, you need to understand the cause first and control it. Some effective fixes include chemical controls, proper mowing, correct fertilizer application, dethatching, and increasing exposure to sunlight if you’re not growing a shade-tolerant turfgrass.
1. Apply a fungicide on your lawn
If the grass whitening is due to powdery mildew, spraying the lawn with a fungicide treatment will reduce or totally eradicate infection. Fungicides that contain sulfur, neem oil, and triforine are the most effective on powdery mildew. An eco-friendly, non-toxic alternative is baking soda (potassium bicarbonate) mixed with a mild horticultural oil.
2. Adopt better Mowing Practices
To fix grass whitening caused by excessively low mowing heights, adjust your mowing height to avoid cutting off too much of the grass blades. As a rule of thumb, never cut off more than 1/3 of the length of the grass leaf blades. This leaves behind enough grass blade surface area to facilitate photosynthesis, allowing the grass to make ample food for itself.
Meanwhile, if your grass is turning white due to damage caused by dull lawnmower blades, sharpen the blades or use one that produces clean cuts. You should sharpen the blades after every 20-25 hours of use. Sharper blades result in a precise, clean cut that leads to lesser damage on the grass blades.
You may also want to replace your mower blades after one or two growing seasons depending on the frequency of use.
3. Dethatch the lawn
To minimize the presence of white grass caused by Fusarium patch or Fusarium blight, consider dethatching your lawn as both of these diseases thrive in heavily-thatched turfs.
To effectively dethatch your grass turf, use a power rake, hand rake, or a vertical mower (verticutter).
Caution: Power rakes aren’t recommended for use on grass types that spread via stolons as they’ll cut the stolons as well, resulting in extensive turf damage. I recommend dethatching St. Augustine grass strictly using a verticutter and only when necessary.
4. Increase sunlight exposure in your lawn
If your grass is turning white due to either powdery mildew or Fusarium patch, you can fix the problem by increasing the light intensity or the number of hours the grass receives sunlight, as both diseases thrive in shaded conditions.
Trim overhanging branches and canopy to reduce shade in your lawn and allow more sunlight to reach the grass below. Alternatively, overseed the shaded sections of the lawn with a turfgrass variety that’s shade-tolerant.
Note: Shaded areas can be characterized by a thin lawn that attracts weeds. You want to kill weeds first before overseeding to ensure you establish a healthy lawn.
5. Apply a slow-release fertilizer evenly
If fertilizer burns are causing your turf grass to spot white stripes, you can fix the problem by modifying your fertilizer application practices. This entails spreading the fertilizer evenly across the lawn to avoid buildup in certain spots, waiting until the turf is dry to apply fertilizer, and watering the turf immediately after applying fertilizer to soak the granules deeper into the soil.
I also recommend using organic, slow-release fertilizers for your lawn such as Milorganite instead of synthetic ones to prevent burning grass blades and making them turn white.
Each of these measures will minimize the chances of fertilizer burns in the future. A proper fertilizer regimen also reduces the chances of feeding the lawn with too much fertilizer at a time.
6. Adjust the soil pH to suit your turfgrass variety
As earlier mentioned, your grass may be turning white due to iron deficiency – a common problem in alkaline soil types. If this is the case, you can revive your grass by altering the soil pH from alkaline to slightly acidic (pH of 6.5-7).
To effectively lower your soil pH, you can add various materials including organic lawn top dressing, iron sulfate, sphagnum peat, and elemental sulfur.
7. Water your lawn adequately in summer
For grass whitening caused by drought, consider irrigating your lawn regularly to meet the watering requirements of your turfgrass especially during the dry summer months. You should water the lawn deeply during every irrigation session ensuring you soak up 1”-1.5” of the soil.
You can also help your grass recover from drought by aerating the soil. Well-aerated soil allows water to easily penetrate into the grass root zone.
Can white grass turn green again?
While the actual grass blades that have already turned white won’t turn white again, the new growth that sprouts in their place will be green if the right fix is applied. Sometimes, though, the damage is usually extensive and the turf can’t be revived. If this is the case, you can still revive your grass by reseeding the lawn.
More information
- S. Newman and L.P. Pottorff, Colorado State University Extension: Powdery Mildews
- University of Minnesota Extension: Turf Discolored leaf blades
- Joseph W. Rimelspach and Michael J. Boehm; Ohio State University Extension: Slime Molds on Turfgrass